Diabetes is a chronic disease, which occurs when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin, or when the body cannot effectively use the insulin it produces. This leads to an increased concentration of glucose in the blood (hyperglycaemia). As per a report by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, the prevalence of diabetes in India has been recorded at 11.8%. India is home to an estimated 72.96 million diabetic adults. Also called the diabetes capital of the world, this sugar disease is posing an enormous health challenge for our country. Medical experts suggest that awareness, timely detection, and right management can help patients lead a normal life.
Types of Diabetes
There are mainly three types of diabetes:
- Type 1 diabetes, also known as juvenile diabetes, is a chronic condition in which the pancreas produces little or no insulin. Certain uncontrollable factors like genetics and some viruses may contribute to type 1 diabetes. Although type 1 diabetes usually appears during childhood or adolescence, it can develop in adults too.
- Type 2 diabetes is caused by the body’s ineffective use of insulin. It often results from excess body weight and physical inactivity. This is the most common form of diabetes and is largely preventable. 9 in 10 cases of type 2 diabetes could be avoided by following simple lifestyle changes. Uncontrolled type 2 diabetes can lead to chronically high blood glucose levels, causing several symptoms and potentially leading to serious complications.
- Gestational diabetes is hyperglycaemia that is first recognized during pregnancy. It can lead to serious health risks for both the mother and child and needs close monitoring by a health expert.
Symptoms of Diabetes
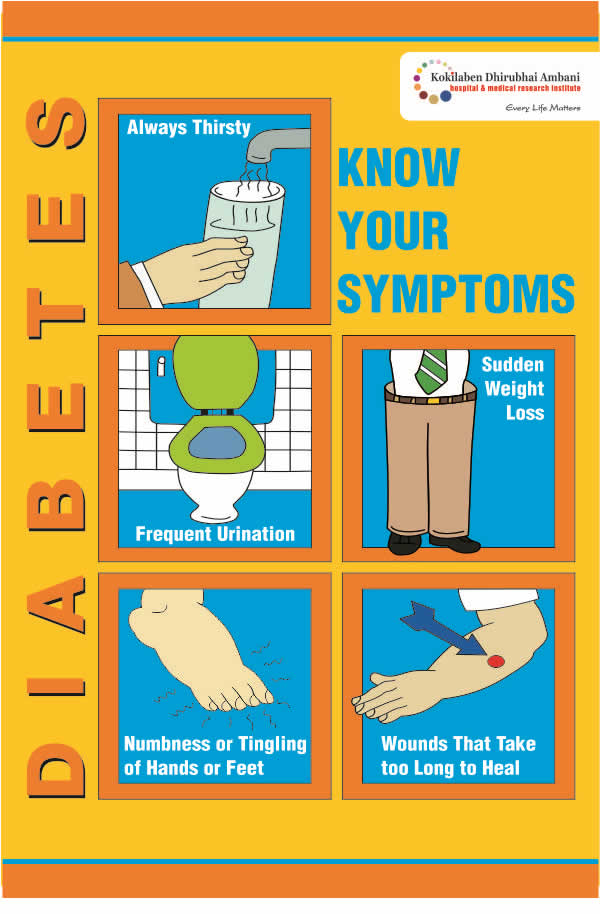
The most common symptoms used to identify diabetes include:
- Increased thirst
- Frequent urination
- Excessive hunger
- Fatigue and weakness
- Blurred vision
- Dry mouth
If you see any of the above symptoms, get your blood sugar levels checked or consult a doctor for further assessment.
Diabetes complications
Uncontrolled blood sugar levels may lead to serious long-term problems affecting the eyes, kidneys, heart, brain, feet, and nerves. These include:
- Eyes – It is recommended that people with diabetes see an eye doctor every year for an eye exam. Eye problems that can occur with diabetes include cataract, glaucoma, retinopathy. Left untreated it may also lead to vision loss.
- Kidneys – It is important to get your urine tested for protein at least once a year. Protein in the urine is a sign of kidney disease. Prompt treatment may slow the changes with kidney disease.
- Heart and brain – All people with diabetes have an increased chance of heart disease and strokes. Heart disease is the major cause of death in people with diabetes. It is important to control other risks such as high blood pressure and high fats (cholesterol), as well as blood sugar.
- Feet – High blood sugar levels can cause skin infections in the foot and leads to slow healing of sores. You can experience severe pain, itching, or experience numbness too. Left untreated, diabetic foot infections may lead to amputation of the toes, foot, or leg.
- Neuropathy – Diabetic neuropathy is a complication of diabetes that results in damage to the nervous system. It is a progressive disease, and symptoms get worse over time.
Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes
Healthy eating and physical activity could help prevent 90% of Type 2 Diabetes cases. Here is what you can do to reduce your risk of getting type 2 diabetes:
- Cut sugar and refined carbohydrates
- Watch your portion size
- Include fibre in your diet
- Exercise regularly
- Drink enough water
- Quit smoking
- Sleep well
- Manage stress levels
- Be regular with health checkups
Diabetes care at Kokilaben Dhirubhai Ambani Hospital
Worried about your fluctuating blood sugar levels? Obesity and a sedentary lifestyle are the most important risk factors responsible for diabetes. It is possible to reduce the burden of type 2 diabetes by lifestyle changes that favour a healthy diet and regular physical activity. Specialists from our Department of Nutrition Therapy can help you with a personalised diet plan. However, certain medical conditions make weight loss difficult and require further intervention.
The Centre for Diabetes and Obesity is equipped with advanced technology and a talented team of experts to help fight obesity and manage diabetes better. For more information, please visit: